Calculating 3PL Fulfillment Pricing

Fulfillment: It’s on every business leader’s mind.
From maintaining optimal inventory levels, to navigating supply chain disruption, to ensuring orders reach customers on time and in perfect condition, order fulfillment is the linchpin to eCommerce operations. And in order to maintain a competitive advantage, businesses need to be able to thread the needle of offering rapid order fulfillment while controlling costs.
In this article, we’ll discuss fulfillment pricing at length — including common costs and how they’re calculated — to help you understand fulfillment pricing models and strike the right balance between customer satisfaction and a healthy bottom line.
- What Are Order Fulfillment Costs?
- What Is a 3PL?
- Common 3PL Fulfillment Costs
- How Are 3PL Fulfillment Costs Calculated?
- Common 3PL Order Fulfillment Pricing Models
- How Legacy Structures Fulfillment Costs
What Are Order Fulfillment Costs?
Order fulfillment costs refer to the various fees that third-party logistics (3PL) companies charge in exchange for their fulfillment services.
What Is a 3PL?
For reference, a 3PL company is a specialized service provider that offers logistics and supply chain management services. These companies handle transportation, warehousing, inventory management and distribution on behalf of their clients, enabling businesses to outsource key aspects of their logistics operations to experts in the field.
Common Fulfillment Costs
3PL providers offer a wide range of services, all of which contribute to fulfillment costs:
- Warehousing: Short- or long-term inventory storage. Many 3PLs offer your choice of dedicated or multi-client warehousing — in other words, the choice to have an entire warehouse dedicated solely to your products, or a warehouse that’s shared between multiple businesses.
- Pick and pack: An order fulfillment technique in which workers pick items from warehouse shelves and package them in individual boxes or envelopes. With pick and pack fulfillment, orders are packaged for shipment and delivery onsite at a warehouse, rather than at a distribution center, eliminating an extra step from the fulfillment process
- Drop shipping: An order fulfillment method in which the merchant doesn’t stock products, but instead relies on their supplier or manufacturer to fulfill customer orders. With drop shipping, when a customer places an order, the merchant sends that order to their supplier, who then fulfills the order directly from their warehouse.
- Last-mile delivery: The final leg of a product’s journey from a distribution center or fulfillment center to its ultimate destination — often a customer’s doorstep. Last-mile delivery can be challenging because merchants must navigate supply chain complexity to ensure on-time delivery and can have a major impact on overall customer satisfaction.
- Kitting and assembly: A popular fulfillment service in which various items, known as child components, are assembled and packaged together to create a kit in preparation for shipment. Some eCommerce businesses choose to create promotional bundles or pre-made kits consisting of products that are often purchased together, while others create kits on demand based on incoming orders.
- Returns management: The process of efficiently handling and coordinating the return of products from customers to the seller or manufacturer. Returns management may include activities such as product inspection, restocking, refurbishing and disposing of goods, with the goal of minimizing customer effort and controlling costs.
In addition to the services list above, other factors that contribute to 3PL costs include:
- Initial setup: Initial setup is a critical first step to establishing a successful partnership with a 3PL and often entails defining goals and objectives, negotiating service-level agreements, integrating systems and other various onboarding procedures. Costs associated with initial setup may include onboarding fees, implementation fees, contract fees and security deposits.
- Inventory intake: Once initial setup and onboarding is complete, you’ll need to move your inventory into your 3PL’s warehouse. This is generally a multi-step process that involves inbound shipping and inventory receiving and comes with associated costs such as shipping rates, container fees and intake fees.
- Account management: 3PL companies not only offer comprehensive service, but also supply chain expertise, often advising their clients on supply chain optimization, carrier selection, risk mitigation, market expansion and so on. Given the level of insights they provide and high-touch service they deliver, 3PLs typically charge administrative fees for account management.
How Are Fulfillment Costs Calculated?
Order fulfillment pricing can vary widely depending on which 3PL you partner with, which services you use, what types of products you offer, your average order volume, seasonality and more.
Though there isn’t a single tried-and-true formula for calculating your actual fulfillment costs, you can generally get an estimate of your anticipated cost per order by adding up the total expense of the various services you intend to use within a given period of time, and dividing that figure by the total number of orders you expect to receive during that same period.
So, for example, let’s say you run an eCommerce business and intend to work with a 3PL for warehousing, picking and packing, shipping and returns management. According to the 3PL, these are the going monthly rates for those services:
- Warehousing: $1,000
- Picking and packing: $1,500
- Shipping: $1,000
- Returns management: $1,500
The total expense for these services is $5,000. Now, let’s say that you expect to receive 1,000 orders during that month.If you were to divide the total expense by the total number of orders, you’d have an anticipated cost of $5 per order.
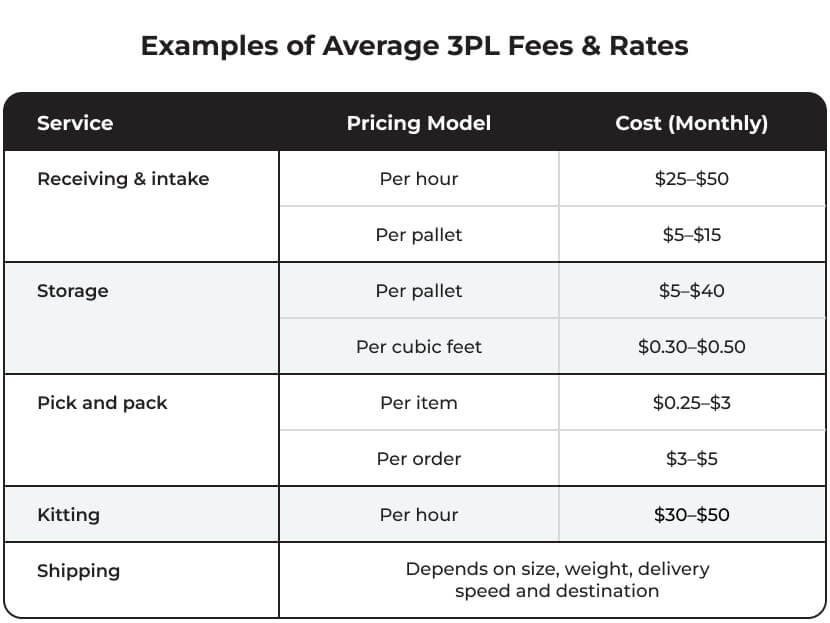
Though these numbers aren’t exact, here are some examples of average 3PL fees and rates according to service and pricing model:
Common 3PL Order Fulfillment Pricing Models
Each 3PL provider takes a different approach to fulfillment services pricing depending on how their business is structured and what services they offer. Here are just a few common examples of 3PL pricing models:
- Transaction-based pricing: The cost of the service is tied directly to the number of transactions or orders fulfilled by the 3PL.
- Per-unit pricing: A 3PL charges clients a specific fee for each individual item or unit it handles, making it easy for clients to calculate costs based on the actual number of products processed.
- Tiered pricing: A 3PL offers different pricing levels based on usage or service tiers, enabling clients to choose the pricing structure that aligns with their specific needs and volumes.
- Volume-based pricing: Clients pay for services based on the quantity or volume of goods that a 3PL stores, processes or ships on their behalf. Volume-based pricing often comes with lower per-unit costs for higher volumes to encourage scalability.
- Fixed pricing: Clients pay a consistent, predetermined rate for a 3PL’s services — regardless of the level of service activity — making it a predictable cost.
- Percentage of revenue: As its name implies, the 3PL charges the client a percentage of the revenue generated from order fulfillment. This pricing model directly ties fulfillment center costs to the client’s sales performance.
- Cost-plus pricing: The 3PL calculates the client’s total fulfillment service costs and adds a predetermined markup or profit margin to those costs to cover its expenses and generate a profit. They then bill the client based on this total cost plus markup.
- Project-based pricing: The 3PL sets a fixed rate for specific, one-time projects or tasks, offering clarity to clients on costs from individual projects outside the regular scope of fulfillment services.
- Customized pricing: The 3PL trailers its pricing structure according to the client’s unique needs and requirements. This approach often results in a personalized agreement that accounts for various factors specific to the client’s business and their products.
Many 3PLs support a variety of fulfillment pricing models and may even apply different pricing models to different services.
How Legacy Structures Fulfillment Costs
Whether you run an eCommerce store, manufacture consumer goods or sell products wholesale, efficient and affordable order fulfillment is an essential component of your business’s operations.
At Legacy, we take a white-glove approach to every aspect of our fulfillment services, including how we structure our costs. We believe in creating tailored fulfillment solutions to meet our client’s unique business needs and prioritize continuous improvement to drive efficiency at every turn.
Ready to start building your own customized fulfillment solution? Contact the Legacy team today to take the first step.
Get Insights. Stay Ahead.
Get the latest news and insights via email on warehouse improvement, transportation optimization, labor strikes and international shipping rate changes.Popular Posts
Search Posts
-
2024 Q1 Freight Landscape: Trends, Challenges, and Predictions
As the first quarter of 2024 comes to an end, here are some observations over the past few months as well as predictions about the trucking...
+ Read more -
Baltimore Bridge Impact Assessment – Update
Following the recent Baltimore Bridge collapse and subsequent port closures, we want to keep our customers informed about the situation and...
+ Read more -
Global Momentum Builds for Charge on Global Shipping Sector’s CO2 Emissions
A growing coalition of 47 countries, including key players like the European Union, Canada, Japan, and various Pacific Island nations, is...
+ Read more